Understanding Tolerance Measurements: A Guide for Inspection Professionals
Modified on:
Understanding Tolerance Measurements: A Guide for Inspection Professionals
Tolerance measurements are crucial in the world of inspection, ensuring that products and components meet the necessary specifications for safety, functionality, and quality. For inspection professionals, understanding how to measure, apply, and interpret tolerance is fundamental to delivering accurate results and maintaining compliance. In this guide, we will explore what tolerance measurements are, why they matter, and how they impact the inspection process.
Here are the Guide for the Inspection Professionals
What Are Tolerance Measurements?
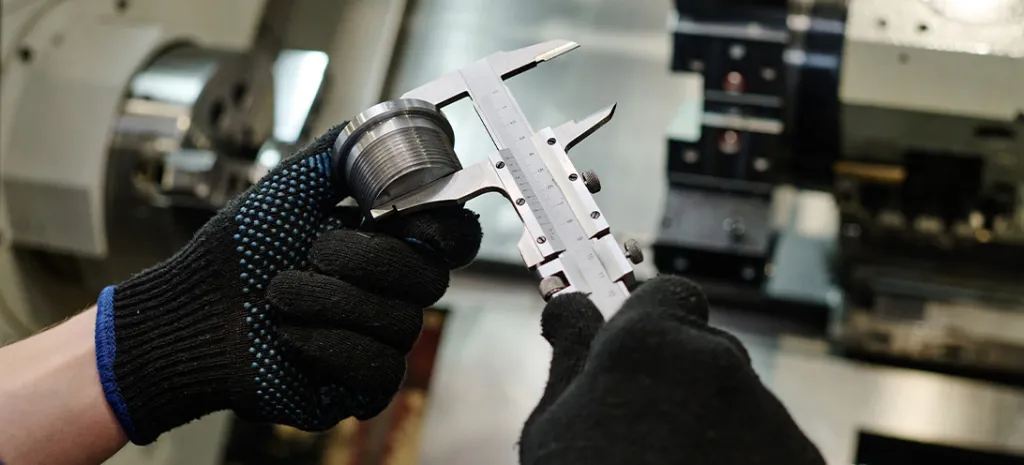
Tolerance measurements refer to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. They define the allowable deviations from the nominal or target measurement that a part can have while still being considered acceptable. Tolerance is critical in industries such as manufacturing and engineering, where precision is key to functionality and safety.
The Importance of Tolerance in Inspections
Tolerance ensures that parts and products conform to design specifications, preventing defects or malfunctions. Without precise tolerance measurements, even small deviations can lead to costly errors, production delays, or product failures. Accurate inspections guarantee that all components fit and function as intended.
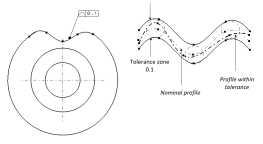
Types of Tolerances: Geometric vs. Dimensional
Tolerances can be broadly categorized into dimensional and geometric tolerances. Dimensional tolerances relate to physical dimensions (e.g., length, width, height), while geometric tolerances describe the shape, orientation, and location of features (e.g., flatness, straightness, roundness). Both are critical in ensuring that parts are functional and meet design specifications.
Common Tolerance Measurement Tools
Inspection professionals rely on a variety of tools to measure tolerance accurately. Common tools include calipers, micrometers, height gauges, and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs). Each tool has specific applications, and knowing which tool to use for different tolerances is crucial for ensuring measurement precision.
How to Interpret Tolerance Values in Inspections
Interpreting tolerance values correctly is essential for inspection professionals. Tolerance values are typically specified in engineering drawings or product designs and indicate the maximum acceptable deviation. Understanding how to interpret these values and applying them correctly during the inspection process ensures that the product meets the necessary standards.
Common Mistakes in Tolerance Measurements and How to Avoid Them
Misinterpreting tolerance values, using the wrong tools, or overlooking small deviations can lead to measurement errors. These mistakes can affect the quality of the final product and increase costs. Regular training, double-checking measurements, and using the right tools can help inspection professionals avoid these common pitfalls.